Table of contents
If you are someone who is new to software development or pursuing a career in software development then you must have already heard a word called "GIT and GitHub". If not let me introduce you to GIT - a version control system. Don't worry I am gonna explain this thing called Version Control System, why it is necessary to learn git, and how it helps Software Developers, Testers, DevOps and many other fields related to Software and its other related areas.
Understanding Version Control System
Tracking changes in the codebase
It is a systematic approach to managing changes in your code. It tracks what changes are made at what time and by whom and can be used to change back to the previous version if needed. Think of it as a tracker that keeps a record of every change made in the code with a UNDO feature.
Enable collaboration with ease
It has also enabled developers to work in collaboration with other developers, different developers can work on different aspects of a project without interfering with each other's work and help merge these changes seamlessly.
Helps in code revision and creating isolated copies
Using VCS developers can create a copy of a codebase/code that is completely isolated, it does not affect the main codebase which provides a safe ground for the experimentation of creating a new feature or fixing a bug properly and merging it to the codebase later without affecting the whole software.
Resolving conflicts
In cases of multiple developers modifying and merging changes, there are situations when the same section of code is modified simultaneously, it helps identify conflicts while maintaining code integrity.
Some examples of VCS are Git, Subversion (SVN), Mercurial, Perforce (Helix Core), Bazaar and Microsoft Team Foundation Version Control (TFCV). But Git has been a go-to choice for developers due to its versatility, and the rise of platforms like GitHub, GitLab and Bitbucket all these platforms work similarly but more importantly they leverage Git for collaborative software development. There is also one more thing that helped Git gain wider adoption, the open-source community.
Installing Git in Local Machine
For Windows
Open Terminal and paste the command below, it will directly download the most compatible version of Git for your Windows machine.
winget install --id Git.Git -e --source winget💡If you are getting an error on the above command check if you have installed Winget Package Manager, click on the link to get step-by-step instructions on installing Winget Package Manager
OR
Open the Link (Click me 🌐), it will redirect to the downloads page of Git and follow the process to download and install Git.
Verify whether Git is installed or not
Open a terminal and write
githit enter it should show similar results as shown below in the attached screenshot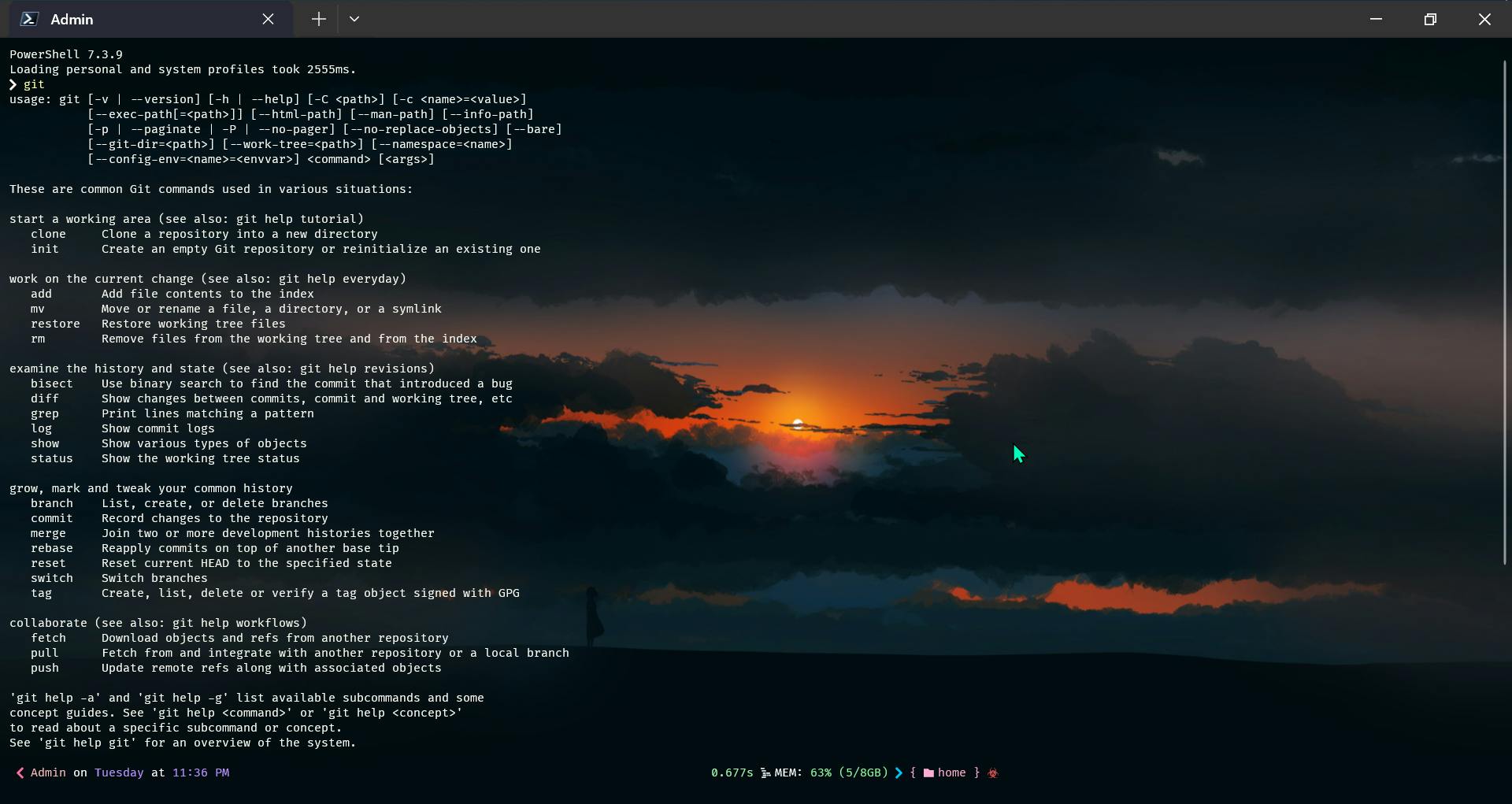
For Linux
Choose your Linux Distro, use the command in the terminal
For macOS
Creating GitHub Account
Fill relevant information like email, password and username
Verify your email and log in to your GitHub account
Create a repo and readme file
Click on the upside-down triangle button and select the new repository

Give a name to your new repository, scroll down and click on
Create Repositorybutton
And Done, Congratulations you have created your first Repository on GitHub.
But your repository is still empty click on README to create a readme.md file (markdown format file), you can describe the repository, then click on the
commit changesbutton to apply changes.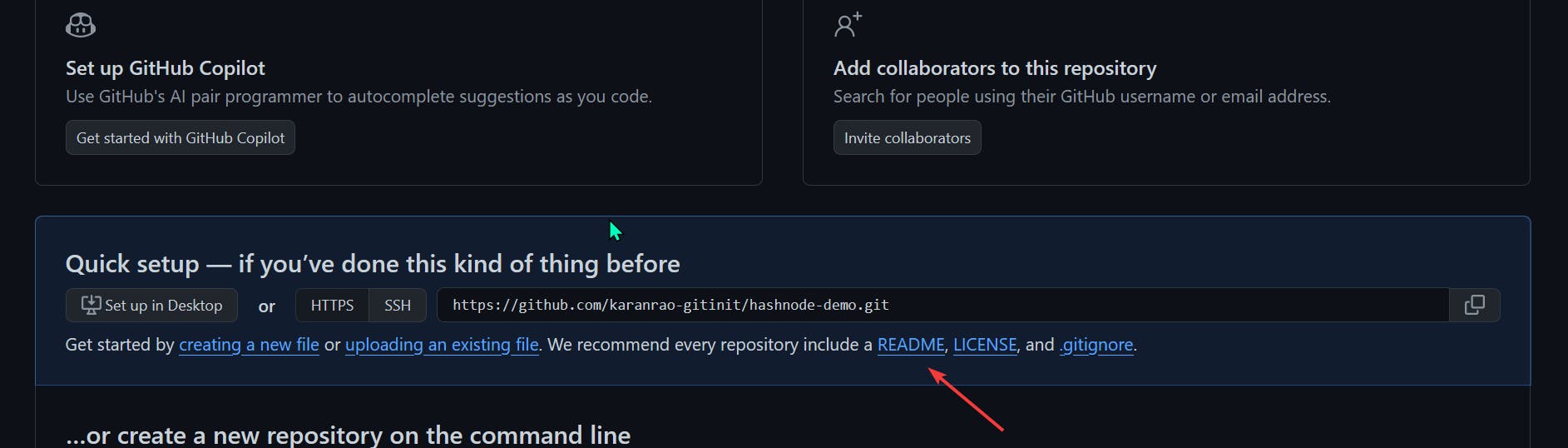
Output
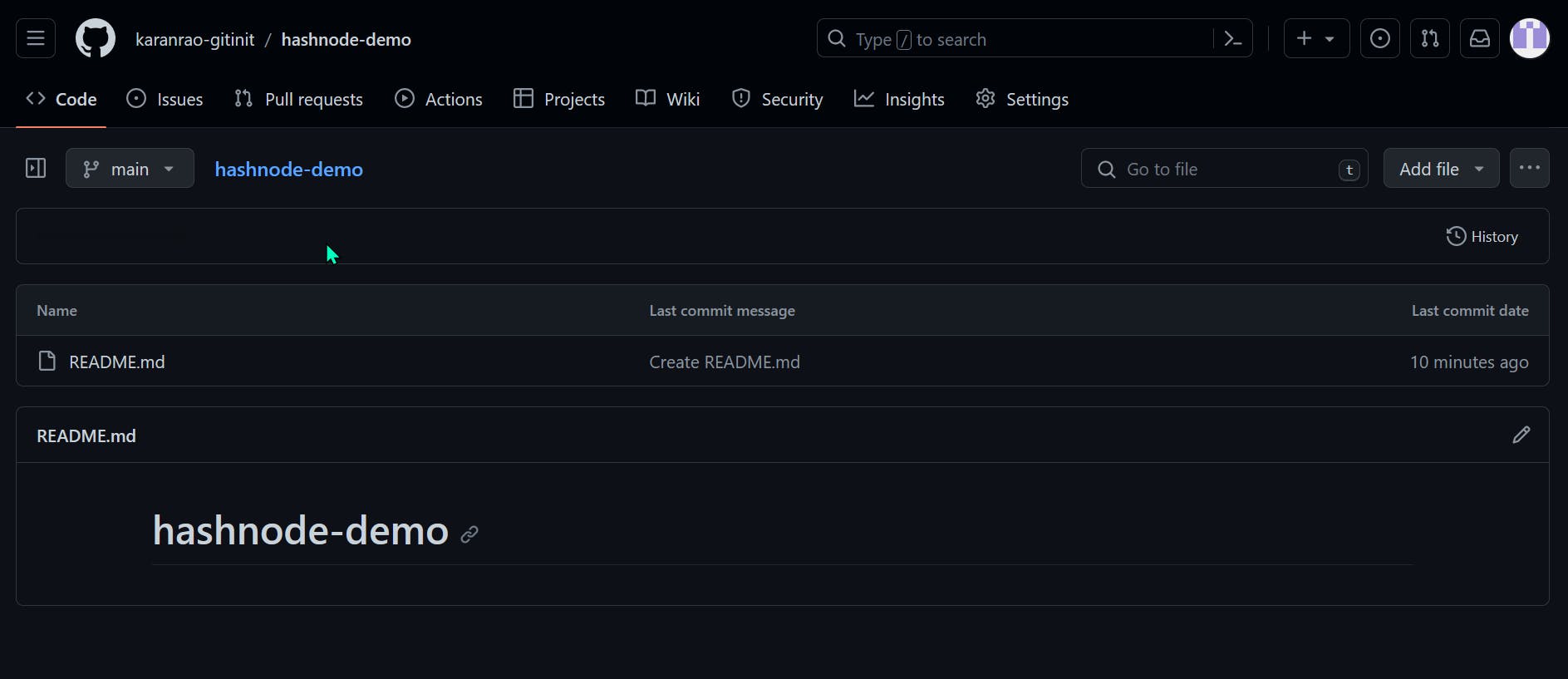
If you have reached this point congratulations you have reached the end of this blog, In conclusion, you have learned about the soul of Git "THE Version Control System", how it helps developers and its main purpose. Installation of Git on a Local machine, setting up a GitHub account and creating a new repository.
For the next part, I will demonstrate How to connect your local machine to GitHub servers, basic git commands to add, remove, and track changes, create new isolated copies of your existing repository, merge them later, and solve merge conflicts.
See you all in the next part.
